How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, opening doors to breathtaking aerial photography, innovative surveying techniques, and exciting recreational pursuits. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding regulations and performing pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight maneuvers and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly and explore the boundless possibilities of drone technology.
We’ll cover everything from the initial unboxing and setup of your drone to mastering advanced features like GPS-assisted flight and obstacle avoidance. We’ll also explore the legal aspects of drone operation, ensuring you fly within the bounds of the law and prioritize safety at every stage. This comprehensive guide is designed for both beginners and those seeking to enhance their existing drone piloting skills.
Drone Regulations and Safety

Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to relevant regulations and safety protocols. This section covers essential aspects of safe and legal drone operation, including licensing, airspace restrictions, pre-flight checks, and best practices.
Drone Licenses and Permits
Drone operation often requires licenses and permits, depending on the type of use (recreational or commercial) and the drone’s weight and capabilities. Recreational users might need to register their drones with the relevant aviation authority, while commercial operators usually require a Remote Pilot Certificate. Specific requirements vary by country and region; it’s crucial to check the regulations in your area.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones, How to operate a drone
Several airspace restrictions and no-fly zones exist to ensure safety and security. These include areas around airports, military bases, and other sensitive locations. Many apps and websites provide up-to-date information on airspace restrictions. Always check before flying.
Pre-Flight Checks for Safe Drone Operation
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe operation. This includes visually inspecting the drone for any damage, checking battery levels, ensuring GPS signal acquisition, and verifying the proper functioning of all motors and sensors. A pre-flight checklist should be performed meticulously before each flight.
- Inspect the drone’s body and propellers for damage.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Verify GPS signal strength and satellite lock.
- Test all motors and ensure they respond correctly.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Review the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
Best Practices for Responsible Drone Operation
Responsible drone operation involves maintaining awareness of your surroundings, respecting others’ privacy, and adhering to all applicable regulations. This includes maintaining visual line of sight with your drone, avoiding flying over crowds, and respecting private property.
Comparison of Recreational and Commercial Drone Regulations
| Regulation | Recreational Use | Commercial Use |
|---|---|---|
| Licensing/Registration | Often requires registration with the aviation authority. | Requires a Remote Pilot Certificate and potentially other permits. |
| Airspace Restrictions | Subject to airspace restrictions and no-fly zones. | Subject to more stringent airspace restrictions and no-fly zones. |
| Operational Limits | Typically limited to recreational purposes and lower altitudes. | May have operational limits based on the type of commercial activity. |
| Insurance | Generally not required. | Usually requires liability insurance. |
Getting Started: Unboxing and Initial Setup
This section guides you through the initial setup process, from unboxing your drone to connecting it to your mobile device and calibrating its sensors.
Drone Package Components
A typical drone package includes the drone itself, a remote controller, a battery, charging cables, propellers (often spares), and instruction manuals. Some packages may also include additional accessories, such as carrying cases or extra batteries.
Charging the Drone Battery and Remote Controller
Charging procedures vary depending on the drone model. Generally, the drone battery and remote controller are charged using separate chargers or via USB. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific charging times and safety precautions. Never overcharge the batteries.
Installing Necessary Software and Apps
Many drones require a dedicated mobile app for control and configuration. Download and install the app from your device’s app store. Ensure the app is compatible with your drone’s model and your operating system.
Connecting the Drone to the Remote Controller and Mobile Device
The connection process typically involves pairing the drone with the remote controller and then connecting the remote controller to your mobile device via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. Follow the instructions in your drone’s manual for the precise steps.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available online; for comprehensive guidance, check out this helpful guide on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable and productive experience.
Remember always to prioritize safety when learning how to operate a drone.
Calibrating the Drone’s Sensors and Compass
Calibrating the drone’s sensors (IMU and barometer) and compass ensures accurate flight performance. The calibration process is usually initiated through the drone’s app. Follow the app’s instructions carefully, typically involving a series of specific movements.
Basic Drone Controls and Flight Maneuvers
Understanding basic drone controls is essential for safe and efficient flight. This section covers the functions of the remote controller and fundamental flight maneuvers.
Remote Controller Functions
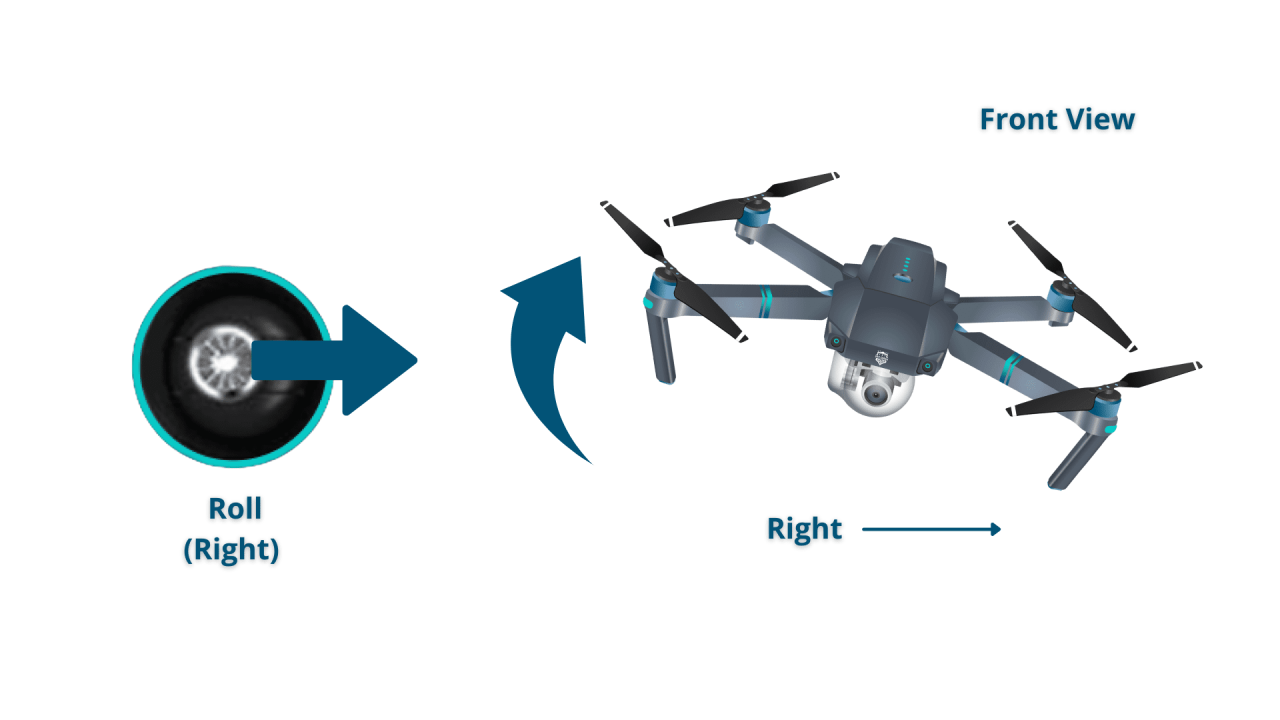
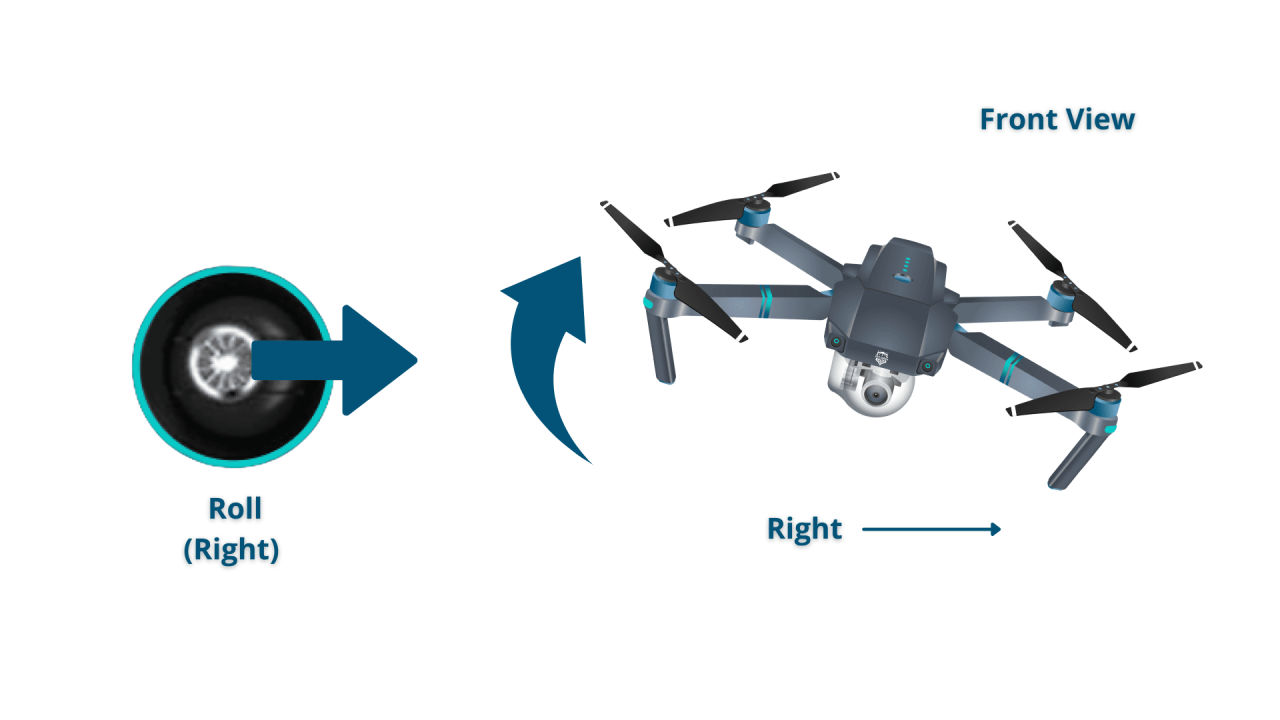
Most drone remote controllers have two joysticks: one controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and throttle (vertical movement), and the other controls the drone’s pitch (forward/backward movement) and roll (left/right movement). Buttons on the controller typically control features like camera operation, return-to-home (RTH), and flight mode selection.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing
Taking off involves gently increasing the throttle until the drone lifts off the ground. Hovering requires maintaining a steady throttle and joystick inputs to keep the drone in a fixed position. Landing involves slowly decreasing the throttle until the drone gently touches down.
Flight Modes
Many drones offer different flight modes, such as beginner mode (which limits speed and responsiveness), and advanced mode (which allows for full control). Beginner mode is recommended for novice pilots.
Maintaining Stable Flight in Different Wind Conditions
Wind can significantly affect drone stability. In windy conditions, reduce speed, fly lower to the ground, and use more precise joystick inputs to maintain control. Consider postponing the flight if the wind is too strong.
Joystick Movements and Drone Response
A visual representation would show a diagram with the joysticks and their corresponding drone movements. The left joystick controls altitude and yaw (rotation), with upward movement increasing altitude and clockwise rotation turning the drone right. The right joystick controls pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right) movement. Pushing the right joystick forward moves the drone forward, pushing it right makes the drone tilt right and move sideways.
Advanced Drone Features and Techniques
This section explores advanced drone features and techniques to enhance your flying experience and capture stunning aerial footage.
GPS, Return-to-Home (RTH), and Obstacle Avoidance
GPS enables precise positioning and allows for features like RTH (automatically returning the drone to its takeoff point), and obstacle avoidance, which uses sensors to detect and avoid obstacles.
Using the Drone’s Camera for Photos and Videos
Most drones are equipped with cameras capable of capturing high-resolution photos and videos. The camera controls are usually accessed via the drone’s app or buttons on the remote controller.
Achieving Smooth and Cinematic Aerial Shots
Smooth and cinematic shots require slow, deliberate movements and careful planning. Avoid jerky movements and use features like smooth tracking or cinematic modes if available.
Planning Drone Flights
Planning a flight involves considering the location, lighting conditions, and desired shots. Pre-flight planning helps ensure you capture the best possible footage.
Drone Camera Settings
Different camera settings affect image quality. Understanding settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture is important for achieving optimal results in various lighting conditions. Higher ISO values are useful in low light, but can introduce noise. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create motion blur.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition and extending its lifespan.
Regular Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance involves cleaning the drone’s body and propellers, inspecting for damage, and checking all connections. Proper storage is crucial to protect the drone from dust and moisture.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues include low battery, GPS signal loss, and motor malfunctions. Troubleshooting involves systematically checking each component and following the manufacturer’s instructions or online resources.
Proper Drone Storage
Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Use a protective case to prevent damage during transport.
Common Drone Parts and Their Functions
- Motors: Provide propulsion for the drone.
- Propellers: Generate thrust and control the drone’s movement.
- Battery: Powers the drone’s systems.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, responsible for stability and control.
- GPS Module: Provides location data for navigation and RTH.
- Camera: Captures photos and videos.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures the drone’s orientation and movement.
Troubleshooting a Drone That Won’t Take Off

A flowchart would visually represent a troubleshooting process, starting with checking the battery, then the propellers, motors, and finally the flight controller and software.
Drone Photography and Videography: How To Operate A Drone
This section explores the art of capturing stunning aerial photography and videography.
Composition, Framing, and Lighting
Effective aerial photography and videography require understanding of composition, framing, and lighting. The rule of thirds, leading lines, and proper exposure are key elements for creating visually appealing images.
Capturing Stunning Aerial Footage
Capture stunning footage by choosing interesting locations, using proper lighting, and employing creative camera angles and movements.
Editing Drone Footage
Editing drone footage involves using video editing software to enhance the footage and create a compelling narrative. This includes color correction, stabilization, and adding music and sound effects.
Camera Angles and Storytelling
- High-angle shot: Provides a broad overview of the scene, emphasizing scale and context.
- Low-angle shot: Creates a dramatic effect, making the subject appear larger and more powerful.
- Tracking shot: Follows a subject as it moves, creating a sense of dynamism.
- Orbiting shot: Circles around a subject, providing a 360-degree view.
Effective Camera Movements for Cinematic Aerial Shots
A visual guide would demonstrate smooth, deliberate camera movements, such as panning, tilting, and tracking, emphasizing the importance of slow, controlled movements for a cinematic effect. It would showcase how different camera movements can create a sense of motion and draw the viewer’s eye to specific points of interest within the scene.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which provides comprehensive guidance. This knowledge ensures safe and responsible drone operation, maximizing its potential while minimizing risks.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. By understanding the regulations, mastering the controls, and prioritizing safety, you can unlock the immense potential of drone technology. This guide has provided a foundation for your journey into the exciting world of aerial exploration. Remember to always prioritize safety, respect airspace regulations, and continue practicing to refine your skills.
The skies await!
Clarifying Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes and stability features are available. Look for drones with GPS and automatic return-to-home functions.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
Charge your drone battery after each flight and avoid completely depleting it to prolong its lifespan. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal?
If you lose GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower altitude and attempt to regain signal. If unsuccessful, carefully land the drone in a safe area.
How do I clean my drone propellers?
Gently clean your drone propellers with a soft cloth and mild detergent. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.